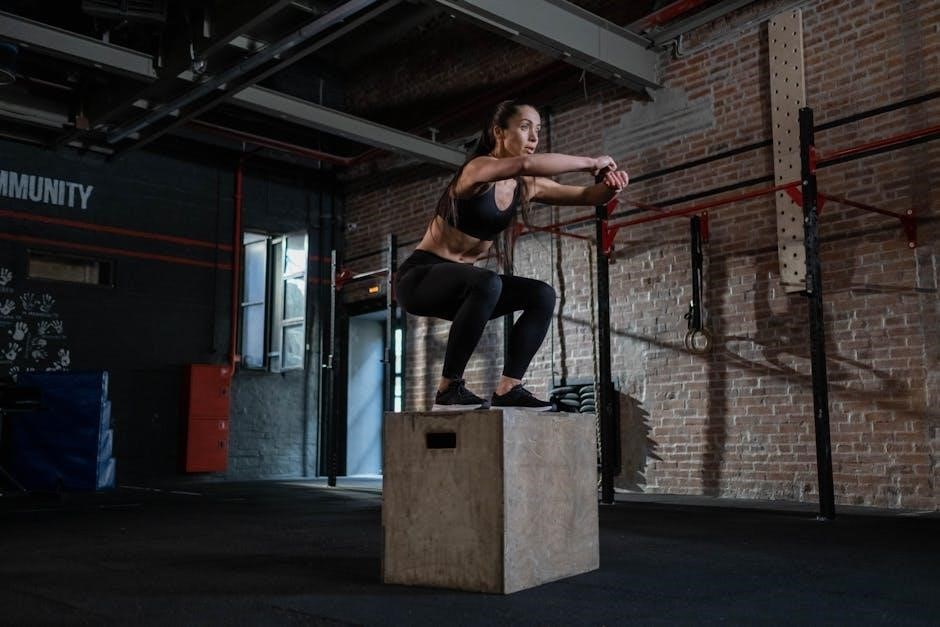
Plyometric workouts are high-intensity exercises that enhance explosive power, speed, and agility. They involve rapid, dynamic movements like jumps and hops, boosting fat loss and muscle strength. A well-structured 4-week plyometric program helps improve performance, with exercises like box jumps and burpees. These workouts are ideal for athletes seeking to elevate endurance and power, ensuring a comprehensive fitness transformation. Proper technique and safety are crucial to maximize results and prevent injuries.
1.1 What Are Plyometric Exercises?
Plyometric exercises, also known as “jump training,” involve rapid, high-intensity movements that enhance muscular power and explosiveness. These dynamic actions, such as box jumps, burpees, and depth jumps, require quick muscle contractions, improving speed, agility, and overall athletic performance. Plyometrics are versatile, suitable for both fitness enthusiasts and athletes, and are a key component in many workout programs designed to boost strength and endurance efficiently.
1.2 Benefits of Plyometric Training
Plyometric training enhances muscular power, speed, and agility while improving overall athletic performance. It boosts caloric burn, increases endurance, and strengthens muscles. Regular plyometric workouts also improve coordination and reaction time, making them ideal for both athletes and fitness enthusiasts. The high-intensity nature of these exercises ensures efficient results, helping individuals achieve their fitness goals faster and more effectively.
1.3 Importance of a Structured Program
A structured plyometric program ensures progressive overload and balanced training, preventing plateaus and injuries. It guides athletes through specific phases, from foundational exercises to advanced drills. This approach optimizes performance gains and reduces risks by focusing on proper technique and gradual intensity increases. A well-planned program is essential for achieving fitness goals efficiently and safely.
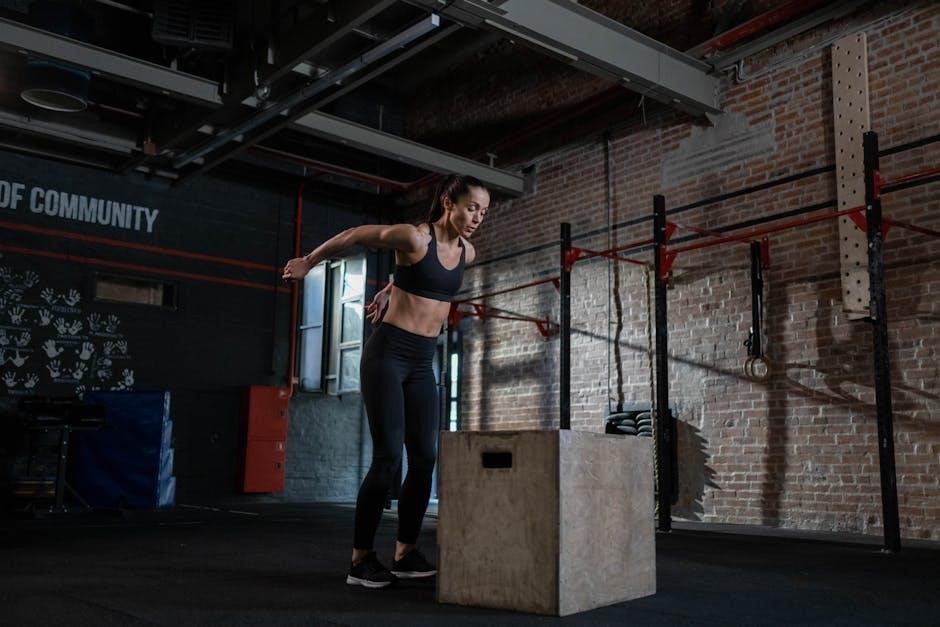

Understanding Plyometric Training Principles
Plyometric training focuses on explosive movements, enhancing power and speed. It involves rapid muscle contractions, improving neuromuscular coordination. Structured programs ensure progressive overload, preventing injuries and optimizing performance.
2.1 Definition and Science Behind Plyometrics
Plyometrics, or “jump training,” involves rapid, high-intensity movements like jumps and hops. It leverages the stretch-shortening cycle, where muscles store energy during eccentric contractions and release it explosively. This neuromuscular efficiency is key to enhancing power, speed, and agility. Science shows plyometrics boosts muscular reactivity, essential for athletic performance and injury prevention, by optimizing muscle-tendon interaction and nervous system coordination. Regular practice enhances overall explosive capabilities.
2.2 Progressive Overload in Plyometric Training
Progressive overload in plyometrics involves gradually increasing exercise intensity to enhance power and performance. This can be achieved by adding height, depth, or complexity to movements. For example, increasing box jump height or transitioning to single-leg drills. Each phase builds on the previous one, ensuring continuous improvement without plateaus. Proper progression ensures mastery and reduces injury risk, optimizing explosive power development effectively.
2.3 Role of Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are critical in plyometric training to allow muscles and nervous systems to rejuvenate. Adequate rest between sets and sessions prevents overtraining and injury. Techniques like stretching, foam rolling, and sleep support recovery, ensuring optimal performance in subsequent workouts. Proper recovery enhances explosive power and overall training effectiveness, making it a cornerstone of successful plyometric programs. Consistency and patience yield the best results.
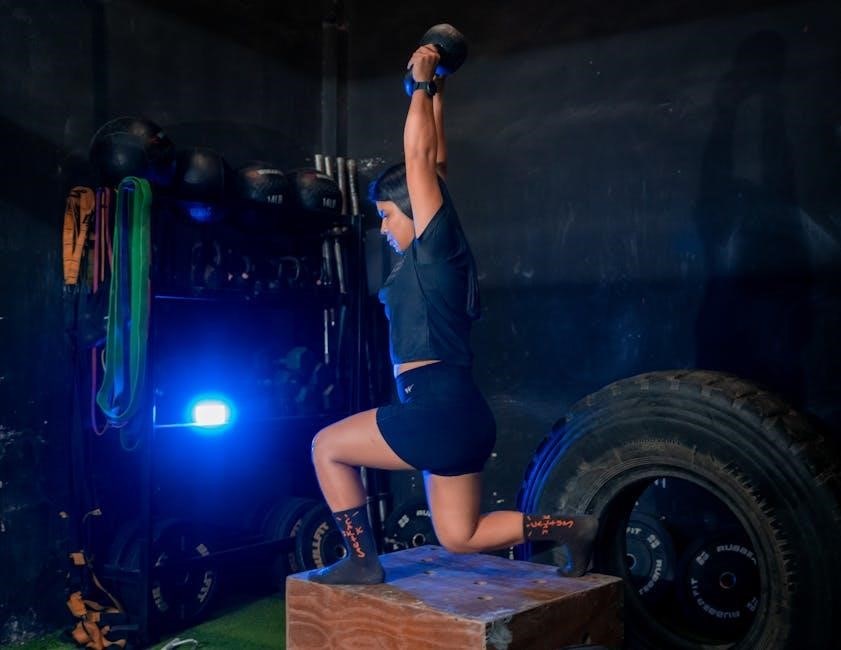

Designing a Plyometric Workout Program
Designing a plyometric workout program involves setting goals, structuring routines, and incorporating exercises that enhance power and agility. A well-planned program ensures progressive overload and optimal results.
3.1 Setting Training Goals and Objectives
Setting clear goals is essential for a successful plyometric program. Whether aiming to improve explosive power, boost endurance, or enhance agility, defining objectives helps tailor workouts to specific needs. For example, athletes might focus on increasing jump height or sprint speed. By aligning exercises with these goals, individuals can track progress and achieve measurable results effectively.
3.2 Structuring a Weekly Plyometric Routine
A well-structured plyometric routine typically follows a 3-day program, focusing on different aspects like lower body power, agility, and full-body explosiveness. Each session includes dynamic warm-ups, foundational exercises, and progressive drills. For example, Mondays might target explosiveness, Wednesdays agility, and Fridays overall power. Incorporating rest days ensures proper recovery, allowing muscles to adapt and strengthen. Consistency and progression are key to achieving optimal results safely.
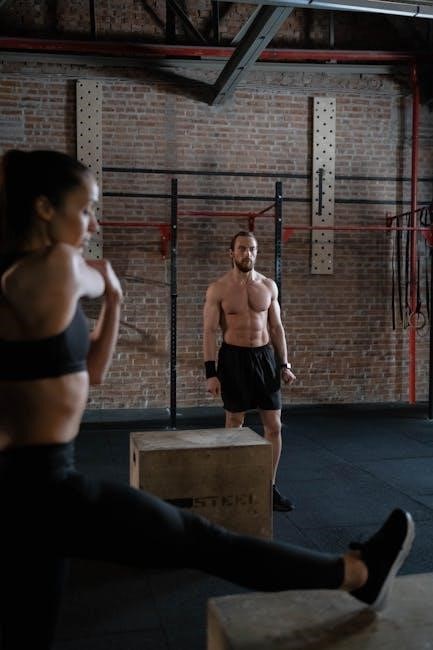
A proper warm-up before plyometric training includes light cardio like jogging, followed by dynamic stretches such as leg swings and high knees. Muscle activations like glute bridges prepare the body for explosive movements. Post-workout, a cool-down with static stretches, foam rolling, and deep breathing aids recovery, reducing muscle soreness and improving flexibility. This routine ensures safety and enhances performance. Box jumps, burpees, and jump squats are essential plyometric exercises that build explosive power and strength. These movements enhance muscle endurance and overall athletic performance effectively. For beginners, basic plyometric exercises include bodyweight jumps, step-ups, and lateral shuffles. These movements focus on building foundational strength and coordination. Start with low-impact variations like squat jumps or small box jumps to ensure proper technique. Gradually increase intensity as comfort and confidence grow. Consistency and form are key to safely progressing in plyometric training. Advanced plyometric drills like depth jumps, burpees, and lateral box jumps challenge athletes to enhance power and speed. These exercises require precision and strength, focusing on explosive movements. Incorporating single-leg hops and plyometric push-ups can further improve agility and endurance. Proper technique and progression are essential to maximize performance and minimize injury risk in these high-intensity drills. Sport-specific plyometric movements are tailored to enhance performance in particular sports. For basketball, box jumps and depth jumps improve vertical leap, while lateral jumps benefit tennis and soccer players. High knees and sprint drills are ideal for runners and football athletes. These exercises mimic game scenarios, ensuring targeted improvements in speed, agility, and explosive power, making them essential for sport-specific training programs. This structured program builds from foundational movements to advanced explosive drills, focusing on power, agility, and endurance over four progressive weeks. Week 1 focuses on building a foundation with basic plyometric exercises. Start with low-intensity drills like bodyweight squats, glute bridges, and basic lunges. Incorporate simple jumps and box steps to adapt your muscles. Perform 3 sets of 8-10 reps, resting 60 seconds between sets. Emphasize proper landing techniques to prevent injury and ensure a safe progression into more intense workouts. In Week 2, gradually increase the intensity by introducing more dynamic exercises like lateral box jumps and burpees. Aim for 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps, reducing rest periods to 45 seconds. Incorporate variations in jumping drills to enhance power and agility. Ensure proper warm-up and cool-down to maintain safety and effectiveness. This phase builds on the foundation established in Week 1, preparing for advanced movements.
Week 3 emphasizes maximizing power and explosiveness through advanced drills like depth jumps and single-leg hops. Aim for 4 sets of 6-10 reps, with 60-second rests between sets. Incorporate plyometric exercises that target specific muscle groups, enhancing speed and agility. Ensure proper form to prevent injuries. This phase builds on previous weeks, pushing your limits to achieve peak performance and explosive power. Week 4 is about reaching peak performance with maximal effort exercises like box jumps and burpees. Perform 3-5 sets of 5-8 reps, focusing on explosive power and speed. Incorporate sport-specific drills to enhance agility and endurance. Ensure proper recovery and form to avoid injury. This phase consolidates previous training, preparing you for high-intensity activities and maximizing overall athletic performance. Safety and injury prevention are crucial in plyometric training. Proper landing techniques and adequate rest reduce injury risks. Assessing readiness ensures safe participation and optimal performance. Common injuries in plyometric training include shin splints, knee strains, and ankle sprains. Overuse and improper landing techniques often cause these issues. Ensuring proper form and adequate rest can help prevent such injuries, while strengthening exercises and warm-ups further reduce risks. Addressing muscle imbalances early is key to maintaining long-term training safety and effectiveness. Proper landing and jumping techniques are essential to minimize injury risks. When landing, roll with the movement, keeping knees slightly bent and weight evenly distributed. Avoid letting knees collapse inward or extend beyond toes. Jumping should involve explosive power from the hips and legs, with balanced takeoff and landing; Rest periods between sets ensure optimal performance and safety, while maintaining proper form prevents overuse injuries and enhances overall effectiveness. Assessing readiness for plyometric workouts involves evaluating strength, flexibility, and technique. Perform a movement assessment to identify muscle imbalances or poor mechanics. Ensure proper landing and jumping form before progressing. Start with basic drills and gradually increase intensity. A coach or trainer can help tailor the program to individual needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness while minimizing injury risks through structured progression. Proper nutrition and recovery are crucial for plyometric performance. Fuel your workouts with a balanced diet rich in protein, carbs, and hydration. Prioritize rest, sleep, and post-workout strategies to enhance muscle repair and energy replenishment, ensuring peak performance and sustained progress in your training program. Proper nutrition is essential for optimizing plyometric performance. Focus on a balanced diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats to provide sustained energy. Hydration is key, so drink plenty of water before, during, and after workouts. Incorporate foods high in antioxidants to aid recovery and consider timing your meals to maximize energy levels during training sessions. After plyometric workouts, prioritize recovery to repair muscles and enhance performance. Incorporate stretching, foam rolling, and hydration to reduce muscle soreness. Consume a post-workout meal rich in protein and carbohydrates within 30-60 minutes to replenish energy stores. Ensure adequate sleep to support muscle repair and overall recovery. Proper recovery strategies help prevent injuries and maintain consistent training progress. Sleep is crucial for optimizing plyometric performance, as it aids in muscle recovery and repair. During sleep, the body rebuilds tissues and enhances strength, essential for explosive movements. Lack of sleep can impair power, speed, and coordination, making it harder to perform plyometric exercises effectively. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly to support training and overall performance. Regularly monitor power output, jump height, and exercise volume to assess progress. Adjust intensity and volume based on performance metrics to optimize results and prevent plateaus. To measure power and explosiveness, track vertical jump height, box jump performance, and sprint speed. Use tools like jump mats or apps to monitor progress. Record improvements in exercise volume and intensity over time. This data helps refine the program, ensuring continuous growth in strength and agility, and maintaining an effective training regimen. Consistency in tracking yields better results. Adjust volume by modifying the number of sets, reps, or exercises based on performance and recovery. Gradually increase intensity by adding height, distance, or speed to jumps. Ensure proper rest between sessions to avoid overtraining. Periodically reassess goals and progress to tailor the program effectively, maintaining a balance between challenge and recovery for optimal results. This approach prevents plateaus and enhances performance.
Periodization organizes plyometric training into phases, each focusing on specific goals like building a foundation, increasing intensity, or maximizing power. Each phase lasts weeks to months, allowing progressive overload and adaptation. This structured approach prevents plateau and injury, ensuring consistent improvement. Adjustments are made based on performance metrics and recovery, keeping the program dynamic and effective. This method ensures long-term success and peak performance. Access printable plyometric workout logs and free PDF downloads to track progress and plan routines. Utilize recommended reading and references for advanced training insights and strategies. Utilize printable plyometric workout logs to monitor progress, track exercises, and set goals. These logs help in maintaining consistency, ensuring each session is recorded for better performance analysis. They are essential for staying motivated and adjusting routines as needed, providing a clear roadmap to achieving fitness objectives effectively and efficiently over time. Access free plyometric program PDF downloads to kickstart your fitness journey. These guides offer structured workouts, exercises, and routines tailored for various fitness levels. From basic drills to advanced training, they provide comprehensive plans to enhance power and agility. Downloadable resources are available on fitness websites, ensuring convenience and accessibility for those seeking effective plyometric training programs without cost. Enhance your plyometric training with recommended reading and references. Explore guides like “Plyometric and Speed Training” by David Potach for in-depth insights. Websites offering free PDFs and research articles provide valuable resources. These materials cover exercise progressions, safety tips, and program design, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of plyometric workouts for optimal performance and injury prevention.3.3 Warm-Up and Cool-Down Protocols

Key Plyometric Exercises for Strength and Power
4.1 Basic Plyometric Exercises for Beginners
4.2 Advanced Plyometric Drills for Athletes
4.3 Sport-Specific Plyometric Movements

Sample 4-Week Plyometric Training Program
5.1 Week 1: Foundation and Adaptation
5.2 Week 2: Increasing Intensity and Volume
5.3 Week 3: Power and Explosiveness Focus
5.4 Week 4: Maximal Effort and Performance

Safety and Injury Prevention
6.1 Common Injuries in Plyometric Training
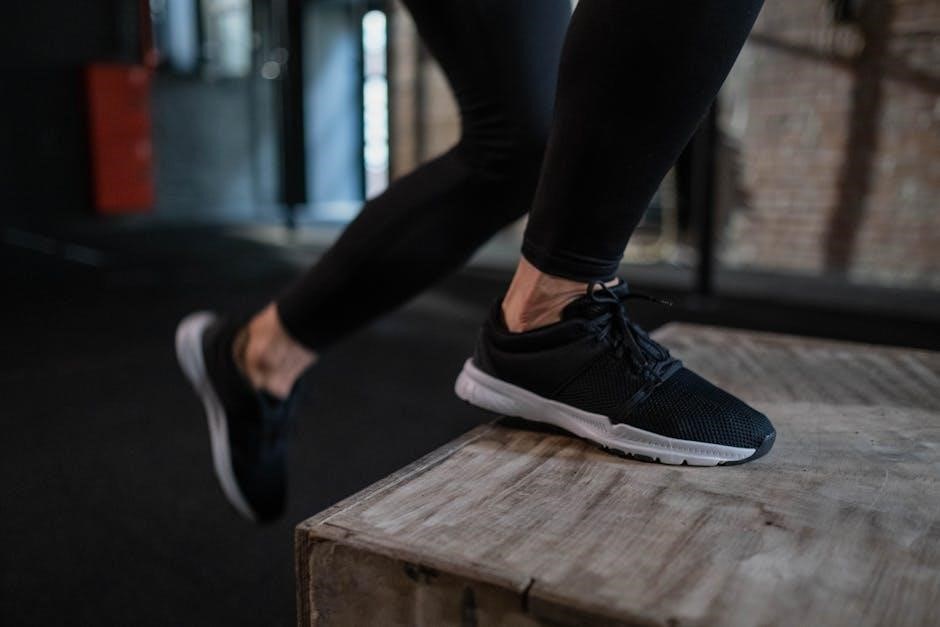

6.2 Proper Landing and Jumping Techniques
6.3 Assessing Readiness for Plyometric Workouts

Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results
7.1 Fueling Your Plyometric Workouts
7.2 Post-Workout Recovery Strategies
7.3 Sleep and Its Role in Performance

Tracking Progress and Adjusting the Program
8.1 Measuring Power and Explosiveness
8.2 Adjusting Volume and Intensity
8.3 Periodization in Plyometric Training

Additional Resources and Guides
9.1 Printable Plyometric Workout Logs
9.2 Free Plyometric Program PDF Downloads
9.3 Recommended Reading and References